OpenSSL
OpenSSL is an open source feature rich command line tool for diagnosing Transport Layer Security (TLS) and Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) protocols. It can also be used to generate self-signed certificates for testing.
Getting started
-
Check if you already have OpenSSL by running this command in the regular OS console.
openssl version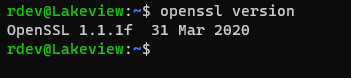
-
If you do not have OpenSSL installed, go to https://www.openssl.org/source/ and download it for your OS. They cover the Windows, MacOS, Linux, and other OSes.
-
If you are on windows, and you have git installed. OpenSSL binaries may have been installed along with git during git's installation, check this location: C:\Program Files\Git\usr\bin for openssl.exe
Basics
-
We can validate the certificate of a website by running the command openssl s_client -connect domain:port#. This will show the certificate chain, server certificate, and other information such as TLS version and cipher used.
openssl s_client -connect google.com:443 </dev/null
The server certificate section in the above screenshot has been truncated.
-
To show the individual certificate in the certificate chains, we can append -showcerts to the previous command to get the certificate chain information.
openssl s_client -showcerts -connect google.com:443 </dev/null
The certificates section in the above screenshot has been truncated.
If the host server is hosting multiple domains on a single IP and it is using SNI (Server Name Indication), we may need to send in the server name by appending -servername domainname.com.
openssl s_client -servername google.com -showcerts -connect google.com:443 </dev/null
Base64 Encoding and Decoding
-
We can use the openssl to encode a string into base64 format.
openssl base64 -e <<< 'SomeText'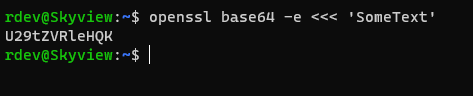
-
We can also use the openssl to decode a base64 encoded string back into plain string
openssl base64 -d <<< 'U29tZVRleHQK'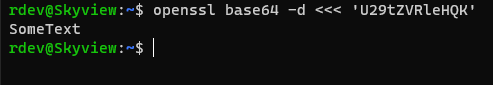
-
We can encode large string into base64 format.
openssl base64 -e <<< 'Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Ornare lectus sit amet est placerat in. Et sollicitudin ac orci phasellus egestas tellus rutrum tellus. Sapien et ligula ullamcorper malesuada proin libero nunc. Urna neque viverra justo nec ultrices dui sapien eget.'
-
When we encode large string into base64 format, OpenSSL word wraps and keeps each line limited to 64 characters. If we want to remove this limitation and have the output in one long line string, we can use -A option.
openssl base64 -e -A <<< 'Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Ornare lectus sit amet est placerat in. Et sollicitudin ac orci phasellus egestas tellus rutrum tellus. Sapien et ligula ullamcorper malesuada proin libero nunc. Urna neque viverra justo nec ultrices dui sapien eget.'
Published on Last updated on